Cybersecurity in Claims Processing: Balancing Innovation with Risk
The digital transformation of insurance has delivered undeniable benefits: faster claims processing, automation at scale, seamless customer experiences, and powerful data-driven insights. Yet with innovation comes risk. As insurers digitize claims, they face a new frontier of cyber threats — from data breaches and ransomware attacks to fraud schemes exploiting interconnected systems.
Claims processing is particularly vulnerable because it sits at the intersection of sensitive customer information, financial transactions, and third-party data sharing. Protecting this ecosystem requires more than traditional IT defenses. It demands a holistic approach to cybersecurity, where technology, governance, and culture converge to safeguard trust while enabling innovation.
The challenge is clear: insurers must embrace digital transformation without compromising security. This balancing act will define the next decade of claims processing.
Why Cybersecurity Matters More Than Ever in Claims
Insurance claims involve vast amounts of personal and financial data. Medical records, bank details, repair invoices, and telematics streams flow across systems and stakeholders. For cybercriminals, this represents a goldmine.
According to industry reports, financial services remain the second-most targeted sector for cyberattacks, with insurance an increasingly attractive entry point. A single breach not only results in financial penalties but also damages customer trust — a currency far harder to regain.
In claims, where speed and accuracy are critical, even a minor security lapse can disrupt operations, delay settlements, and erode the very customer relationships insurers are working to strengthen.
The Double-Edged Sword of Innovation
Digital innovation brings insurers powerful tools to modernize claims. Cloud platforms enable scalable processing. AI automates fraud detection. APIs connect insurers with ecosystems of partners, from repair shops to healthcare providers.
Yet each innovation expands the attack surface. Cloud-based claims systems, if misconfigured, can expose data. APIs, while enabling integration, create potential entry points for attackers. Even customer-facing mobile apps, designed for convenience, can become weak links if not properly secured.
The paradox is unavoidable: the same technologies that drive claims efficiency also introduce new cyber risks. Balancing these forces is now a core strategic priority.
Key Cyber Threats Facing Claims Processing
Data Breaches
Customer data stored in claims systems is a prime target. Breaches can expose sensitive information, triggering regulatory fines and lawsuits.
Ransomware Attacks
Attackers increasingly target insurers with ransomware, encrypting claims systems and demanding payment. The downtime alone can cost millions.
Third-Party Risks
Insurers rely on networks of vendors, repair shops, and healthcare providers. A weak link in this ecosystem can compromise claims data security.
Phishing and Social Engineering
Claims adjusters and customer service staff are frequent phishing targets, given their access to sensitive systems.
Insider Threats
Employees with legitimate access may misuse data for personal gain or fall victim to external coercion.
These threats underscore the urgency of embedding cybersecurity directly into claims transformation strategies.
Building Cyber-Resilient Claims Systems
Zero Trust Architecture
Insurers are increasingly adopting Zero Trust principles — assuming no user or device is trusted by default. Every access request is verified, reducing the risk of unauthorized entry.
Encryption and Data Masking
End-to-end encryption of claims data, coupled with anonymization and masking, ensures sensitive information remains secure even if accessed.
Advanced Monitoring and Analytics
AI-driven cybersecurity tools continuously monitor claims platforms for anomalies, detecting breaches before they escalate.
Third-Party Risk Management
Stronger vetting and continuous monitoring of partners ensures the extended ecosystem does not become a point of vulnerability.
Employee Training
Cybersecurity is as much cultural as technical. Regular training helps employees recognize phishing, manage passwords, and adopt secure practices.
By combining these strategies, insurers create claims systems resilient not only to today’s risks but also to evolving threats.
Regulatory Pressures and Compliance
Cybersecurity in claims is no longer optional; it is mandated. Frameworks like GDPR in Europe, CCPA in California, and NAIC regulations in the U.S. impose strict requirements for data protection and breach reporting.
Non-compliance carries heavy penalties, but more importantly, it undermines customer trust. Insurers must align claims cybersecurity with regulatory expectations, ensuring both legal compliance and reputational protection.
In practice, this means embedding privacy-by-design into claims platforms, conducting regular audits, and maintaining transparent communication with policyholders when incidents occur.
The Economics of Cybersecurity in Claims
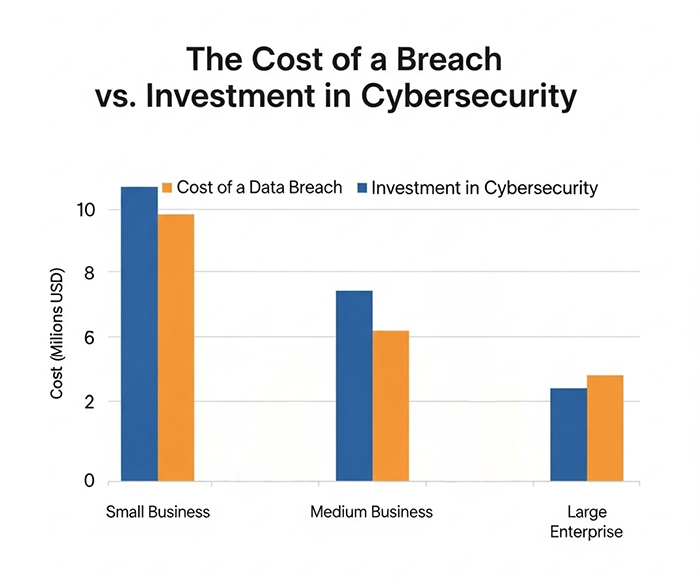
Investing in cybersecurity may seem like a cost burden, but the economics tell a different story. The average cost of a data breach in financial services exceeds $5 million. In contrast, proactive investments in security infrastructure, employee training, and monitoring systems can prevent far greater losses.
Moreover, robust cybersecurity enhances competitiveness. Customers are increasingly aware of data risks, and insurers with strong security reputations differentiate themselves in a crowded market. Cybersecurity in claims is not just about risk mitigation — it is about value creation.
The Human Factor in Cybersecurity
Technology alone cannot solve the cybersecurity challenge. Human behavior remains the weakest link — but also the strongest defense when properly managed.
Insurers must cultivate a culture of cyber awareness, where employees treat data protection as a shared responsibility. This involves ongoing training, simulated phishing tests, and clear escalation protocols when threats are detected.
At the same time, customer education is equally important. Policyholders should be guided on safe digital interactions, such as verifying communications and securing their portals. In claims, trust is built not only through payouts but also through demonstrated data stewardship.
Future Outlook: Securing the Next Generation of Claims
Looking ahead, cybersecurity in claims will evolve alongside digital innovation. Several trends stand out:
-
AI for Cyber Defense: Just as AI drives claims automation, it will power predictive threat detection and automated responses.
-
Blockchain Security: Immutable claims records on blockchain could reduce data manipulation risks.
-
Cyber Insurance Integration: Insurers may bundle cybersecurity with claims systems, both as protection and as a new revenue stream.
-
Collaborative Defense: Industry-wide data sharing on threats will strengthen collective resilience.
The future of claims will not be defined solely by speed and efficiency but by the strength of the digital armor protecting policyholder trust.
Conclusion
As insurers transform claims with digital technologies, cybersecurity emerges as the defining challenge of the digital age. Balancing innovation with risk requires layered defenses, strong governance, and a culture of security awareness.
In an industry built on trust, insurers cannot afford to let innovation outpace protection. Cybersecurity in claims processing is not just a technical priority — it is the foundation of customer confidence, regulatory compliance, and long-term business sustainability.




















